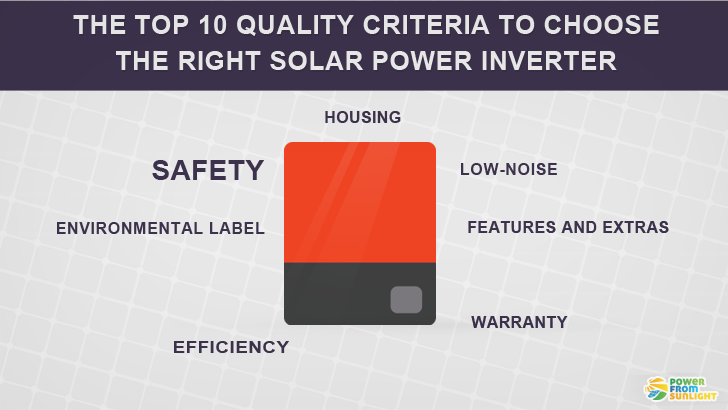
The Top 10 Quality Criteria To Choose The Right Solar Power Inverter
The effectiveness of a solar PV system is decisively influenced by two factors:
- Solar panel efficiency
- PV inverter efficiency
The PV inverter efficiency is more the important out of the two. A solar power inverter with low efficiency can nullify the best efficiency of solar PV panels.
Therefore, careful attention has to be paid to the high quality and the effectiveness when purchasing a solar power inverter.
To objectively choose the right solar power inverter, PV inverter datasheet alone is not always helpful, because it contains different information depending on the manufacturer.
This article provides you with information about the top 10 quality criteria, which will help you to choose the right solar power inverter.
1) Safety of the solar power inverter

Here is checked, how safe the electronic components are. The connections and components shall be so secured that, there is no risk of receiving an electric shock by the user.
In the case of voltage fluctuations (for example by lightning striking), the solar power inverter must be disconnected from the mains to prevent damage.
The solar power inverter should have high safety requirements in accordance with IEC 62109 and UL 1741 (USA).
2) PV inverter housing

The quality of the PV inverter housing will decide on the limit for use. If the solar power inverter is installed outdoors, then the housing must prevent dust and moisture from entering the inverter.
Solar power Inverters with protection class IP65 are suitable for indoor as well as outdoor use.
3) Features and extras
Some solar power inverter models can also assume additional tasks, for example, monitoring the solar panel system and can be connected to a monitor or display so that you can see all important data at a glance immediately.
4) Low-noise operation

Also, the noise emission is a key issue for choosing the solar power inverter. The sound level of the solar power inverter should not exceed 55 decibels. This is the limit, which is in science the transition from low to loud.
If you want to install the solar power inverter in a living space, you should ensure that the device has a low noise emission. Noisy PV inverters do not gain environmental labels.
5) Lifetime and warranty

In addition to the statutory warranty, the PV inverter manufacturers offer a voluntary warranty. Many give a guarantee of five years on their PV inverters, but it is possible to find longer ones.
In principle, the average lifetime of the solar power inverter is at least ten years.
It is extremely likely that the solar power inverter will sustain damage within the lifetime of the solar PV system, and this must be repaired or exchanged.
To minimize the downtimes and costs, you must take a careful look at the warranties of the different inverter manufacturers to see which has a maintenance service included. For an additional charge, the warranty can be extended.
6) Determine AC/DC rated output
Before buying a solar power inverter, you need to know which nominal power the solar PV panels have and how many modules will be installed. With both values, you can calculate the power of the PV array, which must comply with the nominal energy of the solar power inverter.
Calculation example: 10 solar PV panels, with every module having a nominal power of 200 Watt, the total energy of the PV array is 10 x 200W = 2000 Watt.
That means the solar power inverter for these ten solar PV panels requires AC/DC- peak output of at least 2kW.
7) Determine voltage range
It is important to be able to calculate the voltage range of the solar power inverter. Here again, the solar PV panels play a fundamental role.
Example: We use the same above-mentioned module type, which has a voltage range between 29 Volt and 36 Volt.
For ten solar PV panels: 10 x 29V = and 10 x 36V = 360V
That means we need a voltage range between 290 Volt and 360 Volt.
However, to exclude every conceivable eventuality, these values are rounded down and up. As a rule of thumb: -100V for the lowest voltage and +100V for the highest voltage.
So, we need for our solar PV system with ten modules a solar power inverter with a voltage range between 190 and 460 Volt.
A good solar power inverter has a large AC voltage range.
8) Price-performance ratio

The effective cost of the solar power inverter depends on the type chosen and its quality. Typically, we can estimate between 10 to 15 percent of the total investment for the solar power inverter.
High prices of solar inverters should not be the criteria when making a decision. It is necessary to calculate and compare the ratio of other types of inverters as to whether it is justifiable to pay that extra cost or not.
9) Only devices with an environmental label
The solar power inverter must not contain any harmful substances. Devices, which contain problematic substances such as plumb, Cadmium, mercury, bromine or hexavalent chromium, do not gain an environmental label.
Besides, the PV inverter Manufacturer should offer a free take-back of old devices and damaged parts.
A solar power inverter should be on the one hand robust against external disturbances such as voltage surges in the grid due to a lightning strike. On the contrary, the emission of electromagnetic interferences should be low, so they do not affect other devices.

Here IEC 61000-6 and FCC Part 15 (Class A & B) (USA) are relevant.
10) High energy efficiency

The PV inverter efficiency describes the ratio of the amount of power coming out of the solar power inverter to the amount of power coming in.
Because the efficiency is not a fixed value but may vary according to the operating conditions, you should consider different efficiencies. The most meaningful are:
Peak efficiency (maximum)
This is given from the PV inverter manufacturer, usually rated for a specific power level. This value tells you, how much loss the solar power inverter has.
European Efficiency
European efficiency is more significant for practical use because in daily life a solar power inverter must adjust the MPP (maximum power point) of the PV generator and therefore moves in a wide voltage and power range.
The European efficiency is composed of the efficiencies of six different performances, which are weighted corresponding to the frequency of their occurrence (A solar PV system in Northern Europe):
W = W (5%) + W (10%) + W (20%) + W (30%) + W (50%) + W (100%)
CEC efficiency
The California Energy Commission (CEC) has proposed another weighting, which is now specified for some PV inverters used in the US.
Guide you on CEC Efficiency or European Efficiency and not on maximum inverter efficiency. This should be greater than 96%.
Additional Criteria: Certificates
| North America | |
|---|---|
| UL 1741 | Means the Standard for Inverters, Converters, Controllers and Interconnection System Equipment for Use with Distributed Energy Resources. It is the standard applied by Underwriters Laboratories to the product to certify that it meets the requirements of the National Electrical Code®, the Canadian Electrical Code® CSA C22.1; the IEEE‑929‑2000 and IEEE 1547. |
| UL 1998 | The standard for Software in Programmable Components |
| UL 1699B | Photovoltaic (PV) DC Arc-Fault Circuit Protection |
| IEEE 1547 | The standard for Interconnecting Distributed Resources with Electric Power Systems. |
| FCC Part 15 (Class A & B) | This is a part of the Title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations that covers EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) and is regulated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). |
| CAN/CSA C22.2 107.1-1 | Canadian Standards Association Standards, General Use Power Supplies |
| IEC Standards | |
|---|---|
| IEC 62109-1 | Safety of power converters for use in photovoltaic power systems - Part 1: General requirements. |
| IEC 62109-2 | Safety of power converters for use in photovoltaic power systems - Part 2: Particular requirements for inverters. IEC 62109-2 - Specific to inverters Published June 2011 and is being adopted around the world. |
| IEC 61727:2004 Photovoltaic (PV) systems - Characteristics of the utility interface | This applies to utility-interconnected photovoltaic (PV) power systems operating in parallel with the utility and utilizing static (solid-state) non-islanding inverters for the conversion of DC to AC. It lays down the requirements for interconnection of PV systems to the utility distribution system. |
| IEC 62116:2014 Utility-interconnected photovoltaic inverters - Test procedure of islanding prevention measures | IEC 62116:2014 provides a test procedure for evaluating the performance of islanding prevention measures used with utility-interconnected PV systems. This standard describes a guideline for testing the performance of automatic islanding prevention measures installed in or with single or multi-phase utility-interactive PV inverters connected to the utility grid. The test procedure and criteria described are minimum requirements that will allow repeatability. Significant changes concerning the previous edition relate to the DC power source and test conditions. |
| IEC 61000-6-1:2016 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) | • Part 6-1: Generic standards - Immunity standard for residential, commercial and light-industrial environments. • Part 6-2: Generic standards - Immunity standard for industrial environments. |
| IEC 60068-2 Electronic Equipment & Product Standards | IEC 60068 is a collection of methods for environmental testing of electronic equipment and products to assess their ability to perform under environmental conditions including extreme cold and dry heat. IEC 60068 offers appropriate severities and prescribes various environmental conditions for measurements and tests. The procedures below in this standard are typically intended for objects that achieve temperature stability during the test procedure. |