What You Need to Know About Solar Cell Busbar: 0BB, 3BB or 5BB
In this article, we explore one of the most critical components of conventional silicon solar cells: the solar cell busbar.
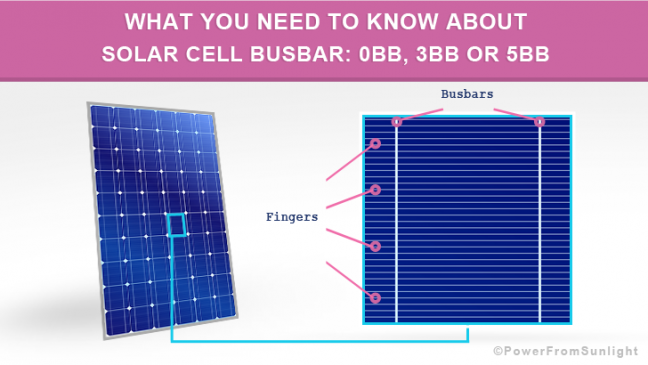
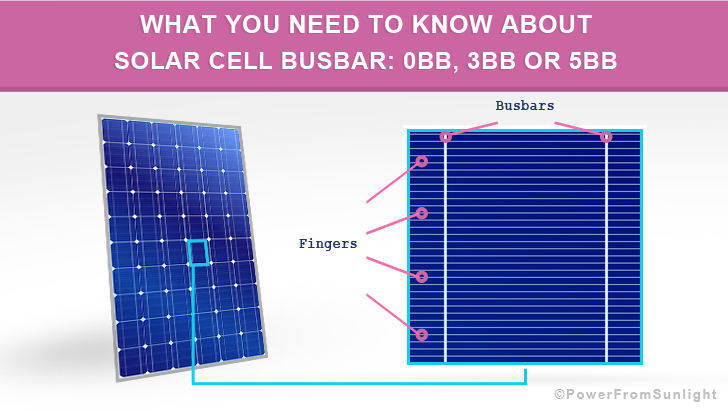
What are solar busbars, fingers, tab wires and bus wires?
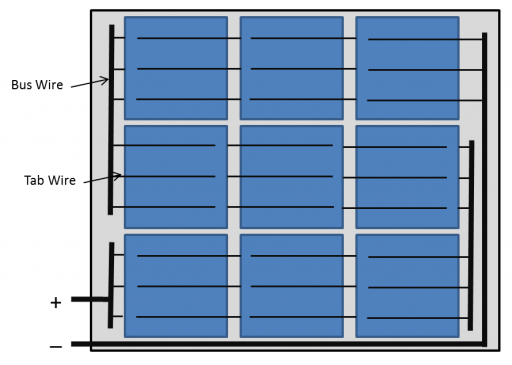
Solar cell busbar
Silicon solar cells are metalized with thin rectangular-shape strips printed on the front and back sides of a solar photovoltaic cell.
These metallic contacts are called busbars and have a significant purpose: they conduct the direct current generated by the solar photovoltaic cell.
Frequently, solar cell busbars are constructed from copper, coated with silver. The silver coating is necessary to enhance current conductivity (front side) as well as to lower oxidization (rear side).
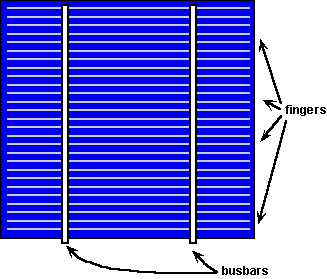
Solar cell fingers
Perpendicular to the busbars are the metallic and thinner grid fingers, also called solar cell fingers, which collect the generated current for delivery to the busbars.
These contacts – the busbars and the fingers – are printed onto the surface of solar photovoltaic cell via a technology called screen printing.
 (Source: http://www.pveducation.org)
(Source: http://www.pveducation.org)
Tab wires
The solar photovoltaic cells have to be connected in series which form rows, to obtain suitable voltages.
The tab wire is brazed either manually or automatically to the solar cell busbar, which connects the individual cells in series with a low series resistance.
The tab wire is also made from round copper wire, by a rolling process and is coated with a layer of solder to permit easy soldering.
Bus wires
Clusters of tab wired cell strings are connected in parallel by bus wires which then deliver the cumulative current from all the cells to the PV junction box.
Because the bus wire has to carry more current than the tab wire, it must also have a larger thickness and width to allow less resistance per unit length.
The bus wire is also made of the same material as the tab wire.
(Source: http://www.the-diy-life.com)
Contact design development
The key trade-off in top contact design is to strike an optimal balance between the increased resistance losses associated with a widely spaced grid and the increased reflection caused by a high fraction of metal coverage of the top surface.
In this regard, the required parameters are the height and width of the busbars, the width of the fingers, distances between the fingers and the busbars, as well as the metal type and quality.
An increasing way in the industry is to re-think cell design and manufacturing which will further improve efficiency and reliability and significantly reduce the material costs – especially regarding the silver paste used in making busbars.
Multi busbar solar cells
3BB busbar solar cells
The most common solar cell design involves three busbars (3BB) printed onto the cell.
5BB busbar solar cells
Five busbars (5BB) cells are currently one of the leading trends in solar cell and module design.
Some sizeable solar panel manufacturers, such as Trina Solar, SolarWorld, and CSUN, increasingly focus their manufacturing on PV solar panels using PERC solar cells with 5BB busbars.
This higher number of busbars reduces the distance between the busbars, which decreases the internal resistance losses.
Even if the higher quantity of busbars increases the shading of the solar photovoltaic cell, the overall performance of multi busbar cells remains much better than that of conventional 2BB or 3BB cells.
The higher number of busbars reduces the effective finger length between the busbars, which decreases finger resistance losses, as well as the impacts of microcracks.
Solar cells are made of very thin wafers, usually about 0.20 mm thick. They have some flexibility but can suffer from pressure induced cracks which are so small they are impossible to see with the eye. These are called microcracks.
(Source: http://solaris18.blogspot.de)
LG’s CELLO wire technology
The multi busbar design with thinner busbars also enables a cost reduction of the expensive silver paste.
An example of this is the LG’s CELLO wire technology. The term CELLO stands for “Cell connection with Electrically Low loss, Low stress, and Optical absorption enhancement.”
LG Electronics has replaced the three standard busbars with 12 round thin circular-shaped wires, which cover the whole surface of the solar cells.
LG’s prime CELLO technology product is its NeON 2 PV module.

(Source: http://www.lg-solar.com)
Busbar-less solar cells
Contrary to the multi busbar concept, other manufacturers such as Solaria are going the entire busbar-less way; the company uses overlapping solar photovoltaic cell segments that are directly electrically connected with each other.
The advantages of busbar-less cells are apparent:
- Reduce inactive space between solar cells.
- More flexible module size design – standard module design is restricted by cell size and spacing requirements
- Significant reduction of power loss caused by shading
- Fewer microcracks, often due to cell soldering
- Saving of busbar material costs

(Source: http://www.solaria.com)
Reduction of busbar material costs
While the multi busbar and busbar-less designs focus on increasing performance and reliability, other approaches focus on the reduction of material costs.
They do this either by minimizing the silver metallization in the busbars – such as with the dash-line busbar designs – or by the entire replacement of silver for the solar cell metallization with alternative materials such as tin or nickel.
Dash-line pattern busbars
In recent years, the industry has come up with a more cost-effective alternative to the standard full line busbars: dash-line pattern busbars, reducing the use of the expensive silver paste.
There are different types of dash-line busbars, such as 3-dash, 5-dash, 6-dash and even 8-dash busbars.
Research has shown that dash-pattern busbars are more sensitive to potential cracking and power degradation – problems that increase with the number of dash lines, with thermal stress accumulating and cracking happening at the corners of a solar cell busbar and thus increasing the number of dashes.

Tab wire optimization: Round wires
Tab wires can also provide an optimizing of the performance of solar cells. This is possible by using round tab wires, which ensure – in comparison to the rectangular-shaped wires – less shading due to their reduced space.