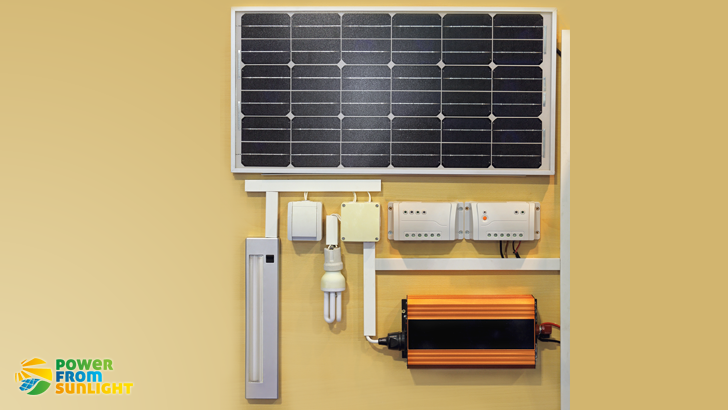
The Most Important Things To Know About Solar Power Inverter (Guide To Choose The Convenable Solar Power Inverter)
This article explains step by step and with an explanation of the differents technical terms in simple way how does solar power inverter work, explains the different types of solar power inverter, the optimale sizing of the solar power inverter and which observation must made by buying a solar power inverter in order to choose the convenable one.
WHAT IS A SOLAR POWER INVERTER AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
Inverter and solar modules are the most important components of a solar PV system.To know more about solar modules and cells, see this article.
Photovoltaic solar cells produce direct current. To be able to use the generated solar power itself or to feed it into the utility grid, a device called a solar power inverter is required,
Solar power inverter has the task of the conversion of direct current into standard alternating current (for grid tied solar systems or if the devices are operated with alternating current).
Another important function of a solar power inverter is the Maximum Power Point Tracking or MPPT.
What is MPPT or Maximum Power Point Tracking?
The technique used in photovoltaics for extracting maximum available power from PV panels under all conditions. Maximum power varies with solar radiation, ambient temperature, and solar cell temperature.
An electronic circuit called an MPP tracker, which is integrated into the solar power inverter in grid tied solar systems or into a charger controller in off-grid solar systems, ensures that the solar modules continuously operate in MPP range.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF INVERTERS?
Depending on the purpose of the solar PV system
They can be categorized into two categories.
- Off grid solar inverter
- Grid tie solar inverter
OFF GRID SOLAR INVERTER
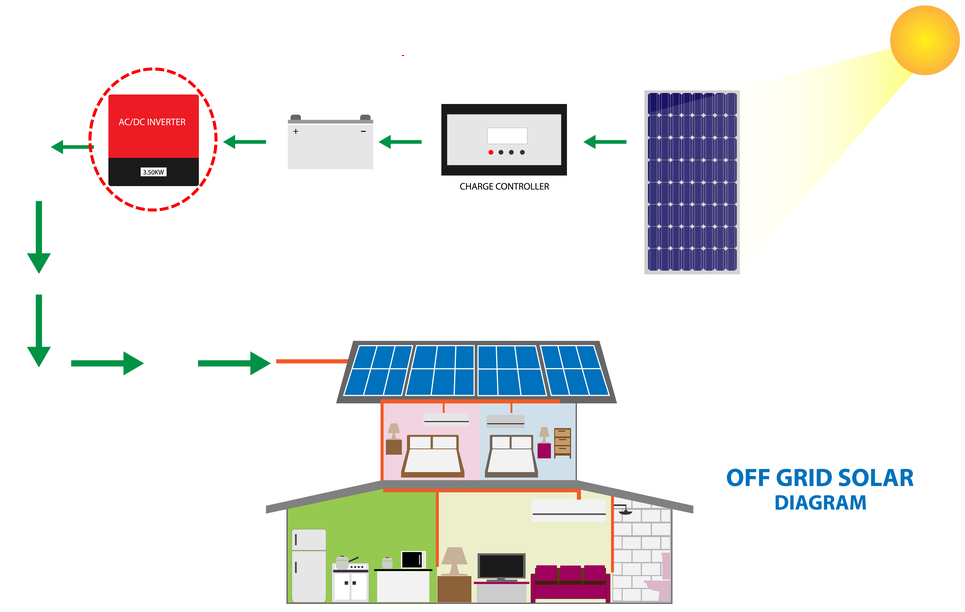
An off-grid solar inverter is also known as stand-alone inverter. In cases where it is only direct current loads which are to be powered, the off grid solar inverters might be lacking in such a system.
In most cases, the off grid solar inverter is used in isolated systems where it draws its direct current energy from the batteries charged by the PV array.
Many off-grid inverters incorporate an integral inverter/charger in order to replenish the battery from an AC source when it is available.
In most cases, these do not interface with the utility grid, and as such, are not required to have an anti-islanding protection (a mechanism by which the grid tie inverter senses whether there is a problem with the power grid such as a power outage.)
When selecting for off-grid solar inverters, it is essential that the output power of the inverter is large enough to support the connected loads.
GRID TIE SOLAR INVERTER
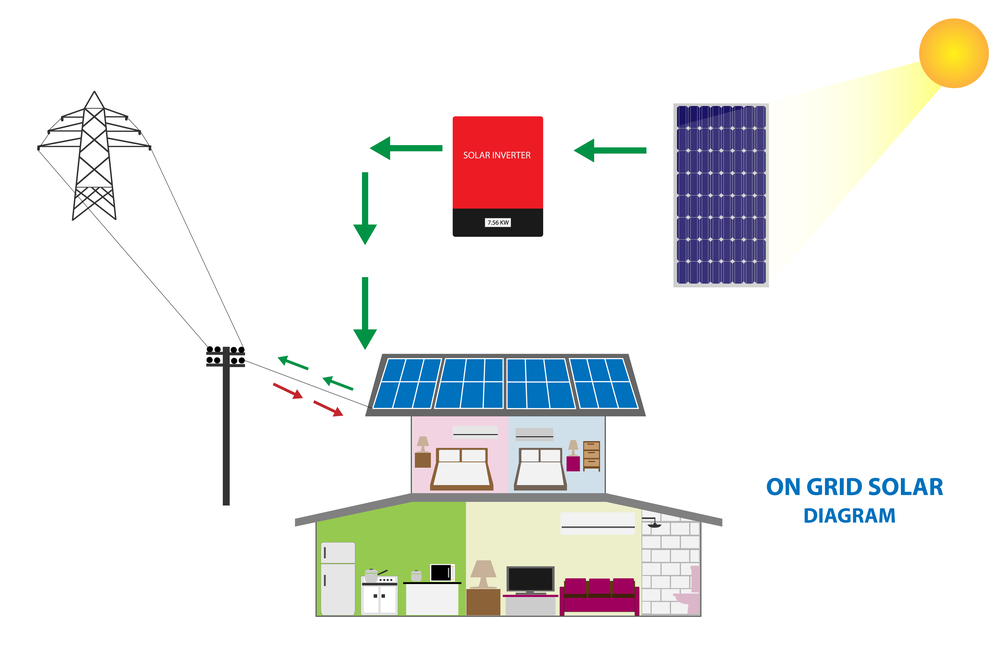
Grid tie solar inverters have to accomplish several tasks which are demanding.
- It links between the PV array and the utility grid or AC loads.
- It adapts the voltage and frequency of the alternating current to the grid.
- It converts direct current into the grid-compatible alternating current with the aid of power electronics and with little losses.
- MPP tracking
- It grants DC and AC protection (reverse polarity protection, overvoltage protection, insulation monitoring, grid and plant protection)
- Monitoring and data logging
Depending on site conditions, solar power inverters can be divided into the following categories:-
- Micro inverter
- String inverter
- Multi string inverter
- Central inverter
Micro inverter

Solar micro inverters are used for a single photovoltaic module. For this, you need many micro inverters. That can be nonetheless useful if the individual solar modules have different orientations and provide very different performances.
Solar micro inverters offer excellent opportunities for optimization, which are designed for small solar PV systems.
String inverter
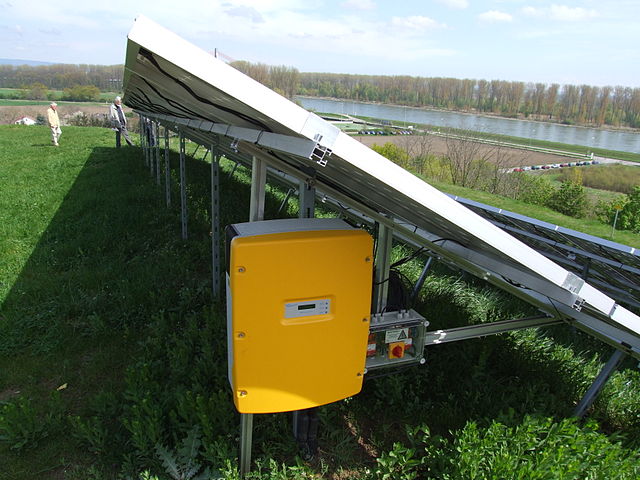

Solar string inverters are very widespread. Several photovoltaic panels are connected in a series and then gathered to string inverter.
They offer an excellent price/performance ratio and are designed for small to medium solar PV systems. Its advantage is that different orientations have less shadowing influence.
Multi string inverter
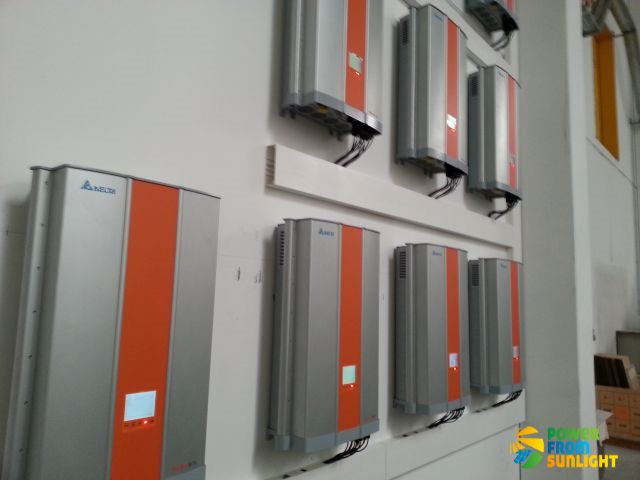

Here, several photovoltaic strings are connected to one inverter. Multi-string inverters have several MPP trackers, and each MPP tracker determines the optimum operating point for each photovoltaic string.
They are an alternative to string inverters for large solar PV systems.
Central inverter
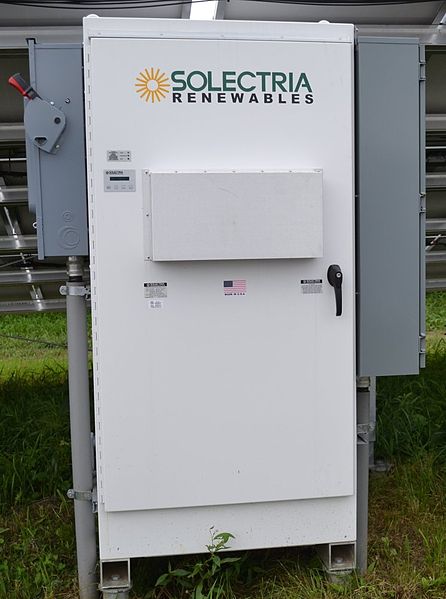

They are used in large solar PV systems and are especially beneficial if the solar power station is very homogenous, in which all photovoltaic Strings have the same inclination and the same direction.
They can achieve high efficiencies and can be well maintained, especially in large photovoltaic plants.
Depending on whether the inverter has a galvanic isolation, which ensures overvoltage protection or not
The solar power inverters are further divided into the following:
Solar transformerless inverter
Most installed inverters are transformerless, with the DC voltage from the PV panels being converted to AC voltage electronically.
Typically the solar transformerless inverters offer better pricing, are smaller, lighter, and usually much more efficient than the solar transformer inverters.
As for disadvantages, the solar transformerless inverters cannot be used universally and are usually not compatible with thin film modules. Besides, to protect against overvoltages, the installation must comply with the electrical protection class II.
Solar transformer inverter
Solar transformer inverters ensure an overvoltage protection, are compatible with all types of solar panels, but they are heavy, expensive und have less efficiency than the solar transformerless inverters.
HOW MANY SOLAR POWER INVERTERS ARE IDEAL FOR A SOLAR PV SYSTEM?
It’s not easy to give a general answer to this question as it is partly a matter of personal preference.
To argue for a one inverter or a few inverters or just one is that the wiring is easier and cheaper and it’s also easy to carry out trouble shooting.
The argument for several inverters is that in case of a defect in the system, the whole solar PV system will not become paralyzed. Besides, they can be excellently adapted to different oriented PV modules i.e. the shadowing problems can be lower.
THE IMPORTANCE OF THE SOLAR POWER INVERTERS FOR THE PLANT OUTPUT
Choosing solar power inverters is decisive for the performance of the solar PV system. The total direct current must be converted from the inverter before it can be fed into the utility grid.
Therefore, the inverter efficiency and its optimal configuration have an enormous impact on the total plant output.
Optimal inverter sizing
Inverter sizing is based on four criteria:
a) Power Input of solar modules
The power, which the solar strings produce, must be lower than the maximum power of the inverter. Usually, it is a factor between module power and rated power of the inverter of 0,9 to 1,2.
b) Maximum number of solar modules
This depends on the maximum input voltage of the inverter. It should be noted that the voltage increases as the temperature falls.
The open-circuit voltage of solar modules should always be under the maximum input voltage of the inverter.
c) Minimal number of solar modules
The voltage of the PV panels reaches its highest value at Maximum Power Point.
The MPP-voltage of the inverter must always be surpassed with the aid of a correspondingly large number of solar panels.
d) Number of parallel PV strings
It is determined by the maximum input current of the solar power inverter because this must always be greater than the solar generator current.
10 Observations Must Made By Choosing a Solar Power Inverter
1. Guide you on European or CEC Efficiency and not on maximum inverter efficiency
Solar power inverters do not always operate at their maximum efficiency, but according to an efficiency profile as a function of the Power.
What is the European Efficiency?
European Efficiency is an averaged operating efficiency over a yearly power distribution corresponding to middle-Europe climate and is now referenced on almost any inverter datasheet.
The value of this weighted efficiency is obtained by assigning a percentage of time to the inverter residues in a given operating range.
If we denote by “Ef50%” the efficiency at 50% of nominal power, the weighted average is defined as:
Euro Efficiency = 0.03 x Ef5% + 0.06 x Ef10% + 0.13 x Ef20% + 0.1 x Ef30% + 0.48 x Ef50% + 0.2 x Ef100%
What is the CEC Efficiency?
For climates of higher isolations like US southwest regions or southern Europe, the California Energy Commission (CEC) has proposed another weighting, which is now specified for some inverters used in the US.
CEC Efficiency = 0.04 x Ef10% + 0.05 x Ef20% + 0.12 x Ef30% + 0.21 x Ef50% + 0.53 x Ef75%. + 0.05 x Ef100%
The two Efficiencies should be greater than 96%.
2. Solar transformerless Inverters are better than transformer inverters
In the solar PV systems with solar transformerless Inverters, residual currents can occur. Therefore, for security reasons, a fault current circuit breaker must be installed.
3. Three-phase solar inverters are usually installed and also in small solar systems.
4. Solar power inverters work better in cooler conditions
The solar power inverter should be installed in an area which is as cool as possible and dust-free, between the PV array and the meters.
5. Solar power inverters for thin film modules
If you use thin film modules, ask your solar installer whether the suitability of a selected solar power inverter (transformer inverter) is in order.
6. The greater MPP voltage range, the better the inverter
The solar power inverter must have a larger performance – control behavior.
7. Noise emissions should be below 40 decibels in residential environments
When solar power inverters have to be installed in residential settings, noise emissions should be a maximum of 40 decibels.
8. Examine the connections and components of the inverter
The concern here is to examine, whether the electrical connections and components are safe so that the user does not receive an electric shock.
9. Inverter housing
The quality of the inverter housing decides on the possibilities for using it.
If the PV inverter must be installed outdoors, then its housing should prevent the penetration of moisture.
Therefore, the solar power inverter should provide a high level of protection conforming to IP65.
10. Lifetime and warranty
In addition to the statutory warranty, inverter manufacturers could offer a voluntary guarantee.
Many give a guarantee of 5 years on solar power inverters, others even more. Generally, solar power inverters have a standard life expectancy of a minimum of 10 years.