How To Easily Read a Solar Inverter Datasheet (Solar Power Inverter Specifications) Part 1: Input Data
This article explains easily how to read the relevant terms in a solar power inverter datasheet (solar inverter specifications) and how valuable this information is in order to choose the best one.
On a closer first look at the solar inverter datasheet, it can appear somewhat confusing, but little by little you will begin to see that the solar inverter datasheet is not that bad.
The following is an example of a solar inverter datasheet, taken with actual values from an SMA SUNNY TRIPOWER 15000TL-US.

On the first page of each solar inverter datasheet, you will find the name of the solar power inverter. It is a good idea to know which solar inverter from which manufacturer is installed in your solar PV system.
The solar PV inverter description usually starts with the name of the manufacturer (Here SMA for SMA Solar Technology AG), then the category of the solar power inverter (Sunny Tripower for three-phase inverter).
Following that the AC nominal power of the solar PV inverter (Here is 15000 Watt, we take Sunny Tripower15000TL-US as an example). US means that this solar power inverter is suitable for application in the USA.
The remainder of the first page often includes an inverter picture and then lists the advantages of this PV inverter, e.g. design flexibility, system efficiency and the additional functions of the solar power inverter.
We will see this in details in the next paragraphs of this article.
If your solar specialist offers you a number of different inverters, look at the solar inverter specifications carefully and check these points.
Technical data
Input (DC)
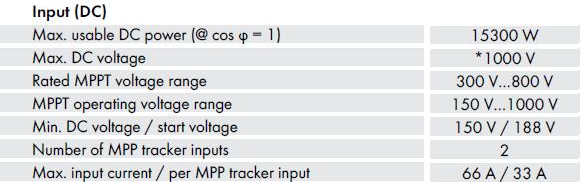
1. Maximum usable DC power (cos(φ) = 1)
DC stands for direct current and refers to the input side of the solar power inverter.
The Maximum usable DC power of the solar PV inverter is defined as the highest power input (here it is 15300 Watt) allowed to flow from the connected PV panels to the solar power inverter, when the power factor is maximal (cos(φ) = 1).
The larger this value is, the better and more expensive is the solar power inverter.
The power factor cos(φ) of an alternating electrical power system is given as a numerical value between 0 and 1 and describes the quantitative ratio of the real power flowing to the load to the apparent power in the circuit.
cos(φ) = 1 means it flows only real power to the load.
2. Maximum DC (input) voltage
This is the maximum allowable voltage on the DC side of the solar PV inverter. This voltage must never be exceeded. If it is, the solar power inverter can be damaged.
The value of the maximum input voltage increases as the temperature decreases and determines how many solar PV panels you can connect in series to the solar power inverter. The value is usually 1000 Volt.
The maximum allowable input voltage number is important to check the solar PV system.
3. Rated MPPT voltage range
The inverter can control the MPP tracking within this voltage range. In other words, the inverter searches for the optimum voltage for the PV generator within this voltage range so that the PV generator produces the maximum power output.
A good solar power inverter has a large MPPT voltage range.
4. MPPT operating voltage range
This is the voltage range in which the solar power inverter can maximize the power extraction from the solar PV system using a technique called Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT).
A good solar power inverter has a large MPPT operating range.
5. Minimum DC (input) voltage / start voltage
The minimum input voltage is the voltage, which the solar power inverter should reach in order to be able to find the Maximum Power Point (MPP) of the PV generator.
The start input voltage of the solar power inverter is the minimum voltage at which the inverter starts pulling power from the PV generator.
The smaller these two numbers are, the better the solar power inverter.
6. Number of MPP tracker inputs
The Sunny Tripower 15000TL-US has two MPP trackers, two inputs A and B. There is one MPP Tracker for each input.
The more MPP Trackers there are, the more expensive the solar power inverter.
7. Maximum input current / per MPP tracker input
In this case, the maximum input current, which flows through the DC side of the solar PV inverter must not exceed the current value of 66 Amper.
Also, the maximum input current per MPP tracker input may not exceed the current value of 33 Amper.